Search Page
The search found 6 results in 0.021 seconds.
Search results
-
NSAIDs for musculoskeletal conditions
There are about 20 different nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) available. Some, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, are widely available over-the-counter (OTC). Others are only available on prescription. NSAIDs are the most frequently used medicines for symptomatic relief in osteoarthritis (OA), the most common form of arthritis, and are often prescribed to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
efaccena - 22/07/2016 - 8:25am
-
NSAIDs (inflammation)
NSAIDs have historically been classified according to their chemical composition, but as mechanism of action has come to the fore, this is also used to classify these drugs.
NSAIDs within classes have similar characteristics and tolerability, with little difference in clinical efficacy at equivalent doses. The prescribers’ choice will be determined by other factors such as dosing regimens, route of administration and tolerability. For example, ibuprofen and diclofenac have half-lives of just 2–3 hours, whereas the oxicams have half-lives 10 times longer.
efaccena - 09/09/2016 - 9:27am
-
Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors
Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), used clinically to relieve fever and pain, such as those associated with headaches, colds, flu, and arthritis. NSAIDs are available by prescription and over-the-counter (OTC).
efaccena - 08/03/2016 - 9:19am
-
Other autacoids
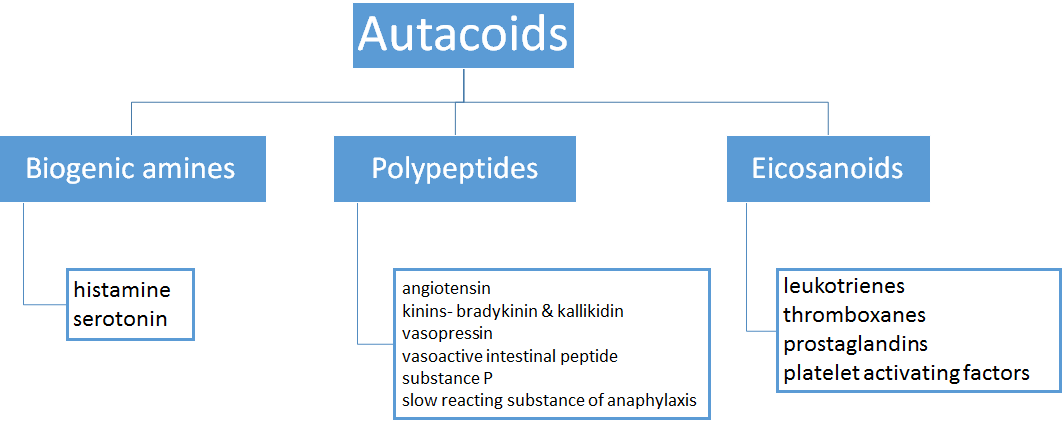
The pharmacology and clinical impact of histamine and serotonin have been described above. This section will focus on other clinically important autacoid molecules.
Autacoids release can be triggered by agents including chemical and immune irritants, UV light, bacterial toxins and physical trauma.
Whilst histamine mediates the wheal, flare and redness reactions, the prostaglandins mediate pain.
efaccena - 29/03/2016 - 1:12pm
-
Migraine
Migraine is a complex condition, but it is characterised as a moderate to severe, pulsating headache that is typically unilateral, and is often accompanied by nausea and disturbed vision (aura). Migraines can last from two hours to several days. Associated symptoms can include nausea and vomiting, as well as sensitivities to light, sound or smell.
Medical intervention is indicated when the migraines become frequent and/or are severe.
efaccena - 22/05/2018 - 11:51am
-
Gasotransmitters
There are many gaseous chemicals with effects/functions in the human body, however only three of these act as bona fide 'gasotransmitters' (or gaseous transmitters): nitric oxide (NO, a free-radical mediator), carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S). These three regulate a variety of key biological functions and are also implicated in tumour biology. They can have endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine actions. They are produced enzymatically under tight regulation. They have varying biological half-lives, which affects their mode of transmitter action.
efaccena - 29/03/2016 - 1:08pm
